Case
Home / Case / Experience / Do you really know the valves commonly used in boiler heating systems?

Case
Industrial boiler heating systems often use a variety of valves. These valves are used to regulate the flow of steam and water through pipes, which helps ensure that the boiler operates properly. Here's a look at some of the most common types of industrial boiler heating system valves:
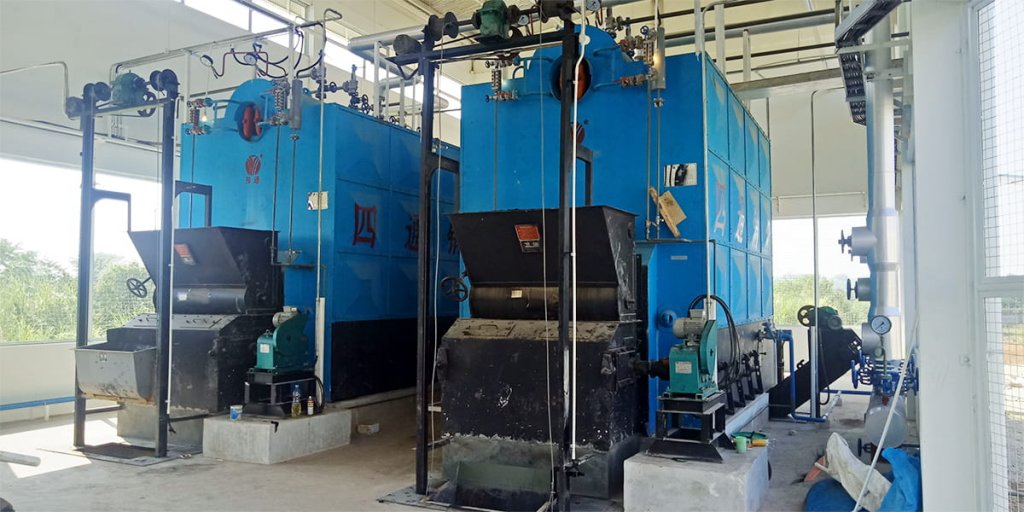

Safety valves are a standard safety device found on most boilers. They are used to protect the boiler from overpressurization and/or excessive temperature. The purpose of a safety valve is to relieve pressure when it exceeds set limits.
Safety valves are required to prevent explosions caused by high pressure in a boiler or pipe, loss of water level due to overheating, thermal shock and erosion of the heating surface caused by excessive heat transfer rate, etc. In liquid-fired boilers, they open when the temperature around them reaches 1% above their rated temperature or 115°C whichever is lower than that. When this happens it allows excess steam to escape through them before damage occurs to any parts inside the system (HVAC Controls).
In many cases, there will be multiple safety valves installed on a boiler at once in order to prevent any one of them from failing and allowing dangerous levels of pressure to build up inside the vessel. Each valve has its own set of gauges so operators can monitor their readings separately from others.
A cast steel globe valve is a kind of cast steel valve, which is used for industrial, domestic, and water supply boilers, hot water heaters, oil and gas production equipment, chemical equipment, and other thermal equipment. It has excellent performance such as high-temperature strength, high corrosion resistance, good seal performance, small vibration force, and so on.
The main material for cast steel globe valve is S45C or S55C steel. The hardness of the surface layer is HRC50-56, that is to say, it can work normally under temperatures up to 150 degrees Celsius. Cast steel globe valves come in two different configurations: 2-way and 3-way. A 2-way valve only allows for the flow of liquid in one direction, while a 3-way valve allows for both directions of liquid flow.
A cast steel globe valve is a gatekeeper, preventing air and other contaminants from entering the system while allowing steam to pass through smoothly. This helps to ensure that high-pressure steam can travel through pipes without causing any damage or strain on equipment.
In addition to controlling the flow of high-pressure steam, cast steel globe valves also help prevent any unwanted liquid from escaping from pipes. This prevents damage caused by leaks and ensures that any spills are contained within safe areas where they can be handled easily by safety personnel.
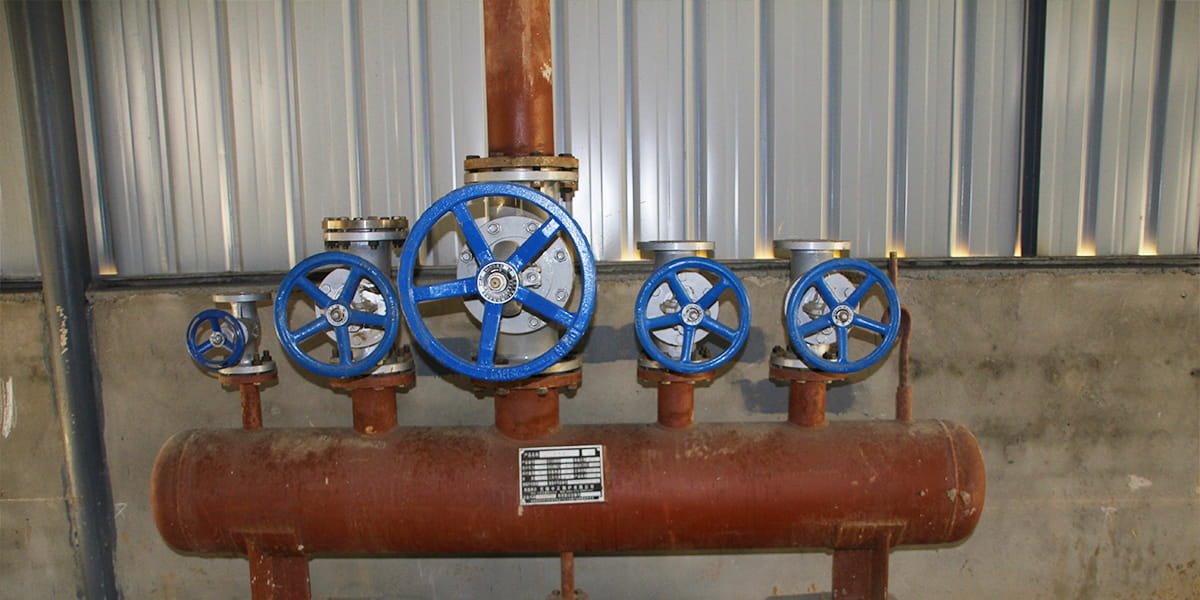
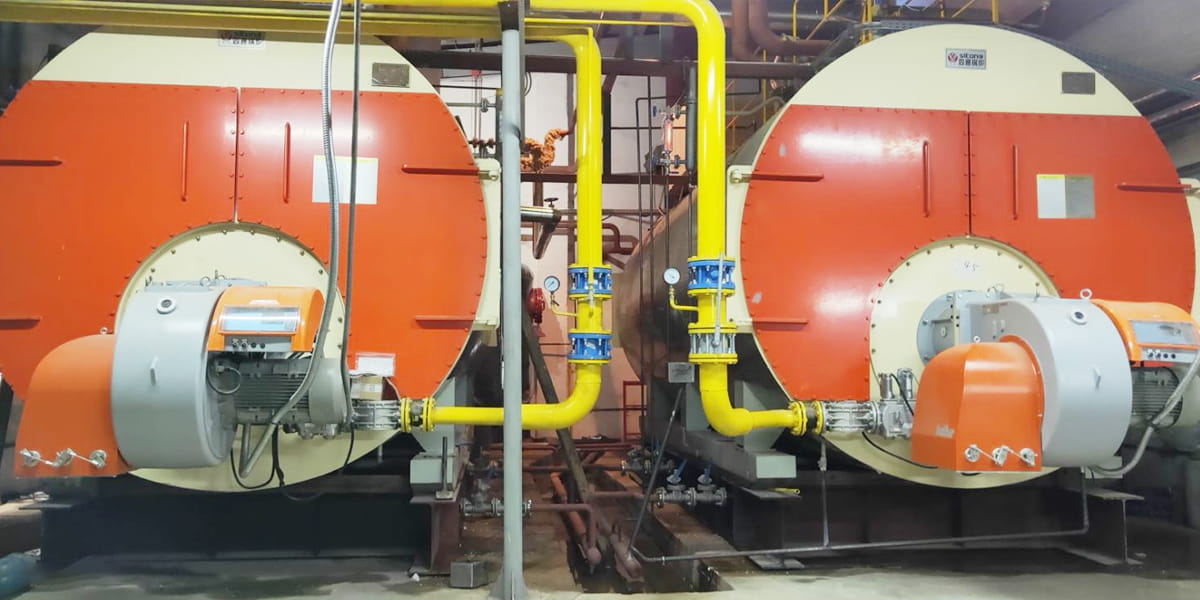


There are many different types of valves on the market today, but one that stands out as particularly useful for industrial boiler systems is a check valve. Check valves work by preventing backflow in a pipe or hose, which means that they're used to stop fluid from flowing backward through the pipe. This prevents damage because it means there's no chance of fluid getting into areas where it shouldn't be. The check valve can also be used as an emergency shutoff device if something goes wrong with your boiler
This means that if something goes wrong with your boiler system—for instance, you turn off your boiler but forget to close off valves on both ends—the presence of a properly functioning check valve will allow you to instantly shut off your entire heating system without having to hunt down each individual open pipe or connector.
Cast steel lift check valves are more commonly used in boiler heating systems. The cast steel material is stronger and more durable than stainless steel and the tighter tolerances of the casting process ensure that the valve will operate correctly for many years with little or no maintenance.
The thread ball valve is one of the most basic valves in the industrial boiler heating system. The thread ball valve has a simple structure and is easy to operate. It can be used for water, gas, and oil.
The thread ball valve consists of a body, stem, and seal ring. The body has three grooves on its outer surface which are used for attaching packing rings. There are two seats inside the body, one at the top and one at the bottom. At the top of the seat, there is a groove for installing packing rings; at the bottom, there is another groove for installing packing rings as well as an opening through which steam can pass through when it is opened. The stem passes through both grooves in order to connect them together so that they can work together as one unit once they’re installed on your boiler system.
Thread ball valves are typically used in industrial boiler heating systems because they don't require much maintenance and can withstand high temperatures. They're also very easy to operate since all you need to do is turn the handle attached to your desired level of flow control, which rotates around its axis and moves up or down depending on whether you want more or less flow. The ball itself sits inside what's called an “outlet” or “inlet” port, depending on how you'd like it positioned; this allows for maximum flexibility so that you can adjust as needed throughout any given day based on demand for steam production versus other needs.
1. Flexible joints
Flexible joints are used to connect pipes in many industries because they can withstand a wide range of temperatures. They are made from various materials such as rubber or plastic that expand or contract when heated or cooled. This is a great advantage when trying to control pressure within a system because it allows for expansion and contraction without causing leaks or cracks in the pipes themselves.
2. Pipeline compensators
The main function of a pipeline compensator is to balance the pressure in the heating system by adjusting the flow of steam. When there are sudden changes in the load on the heating system, such as when a burner is turned off or on, the pressure drops and rises instantly. This causes fluctuations in the process temperature and may cause damage to equipment.
We hope you’ve learned something new and interesting! If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below. We’d love to hear from you.