Case
Home / Case / Experience / Four classifications of stainless steel

Case
304 stainless steel is the most common steel type. As a widely used steel, it has good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties; it has good hot workability such as stamping and bending, and has no heat treatment hardening phenomenon (non-magnetic , then use the temperature -196 ° C ~ 800 ° C).
Household goods (Class 1 and Class 2 tableware, cabinets, indoor pipelines, water heaters, boilers, bathtubs) Auto parts (windshield wipers, mufflers, moldings) Medical equipment, building materials, chemistry, food industry, agriculture, ship parts

As a low-carbon 304 steel, its corrosion resistance is similar to that of 304 steel under normal conditions, but after welding or stress relief, its resistance to intergranular corrosion is excellent; it can also maintain good corrosion resistance without heat treatment. Excellent corrosion resistance, service temperature -196 ° C ~ 800 ° C.
Applied to outdoor machines in the chemical, coal, and petroleum industries that require high resistance to grain boundary corrosion, heat-resistant parts of building materials and parts that are difficult to heat treat.
Due to the addition of molybdenum, 316 stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance, atmospheric corrosion resistance and high temperature strength, and can be used under harsh conditions; it has excellent work hardening (non-magnetic).
Equipment used in seawater, chemical, dye, paper, oxalic acid, fertilizer and other production equipment; photography, food industry, coastal area facilities, ropes, CD rods, bolts, nuts.
As a low-carbon series of 316 steel, in addition to having the same characteristics as 316 steel, it has excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion.316L stainless steel scope of application
Products with special requirements for grain boundary corrosion resistance.
316 and 316L stainless steel are molybdenum-containing stainless steel species. The molybdenum content in 316L stainless steel is slightly higher than that in 316 stainless steel. Due to the molybdenum in the steel, the overall performance of this steel is better than that of 310 and 304 stainless steel. Under high temperature conditions, when the concentration of sulfuric acid is lower than 15% and higher than 85%, 316 stainless steel has a wide range of uses. 316 stainless steel also has good resistance to chloride attack, so it is usually used in marine environments. 316L stainless steel has a maximum carbon content of 0.03 and can be used in applications where annealing after welding is not possible and where maximum corrosion resistance is required.
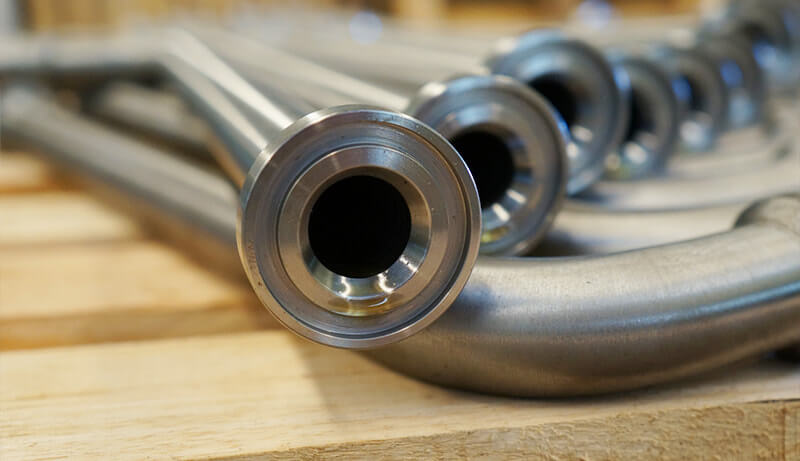
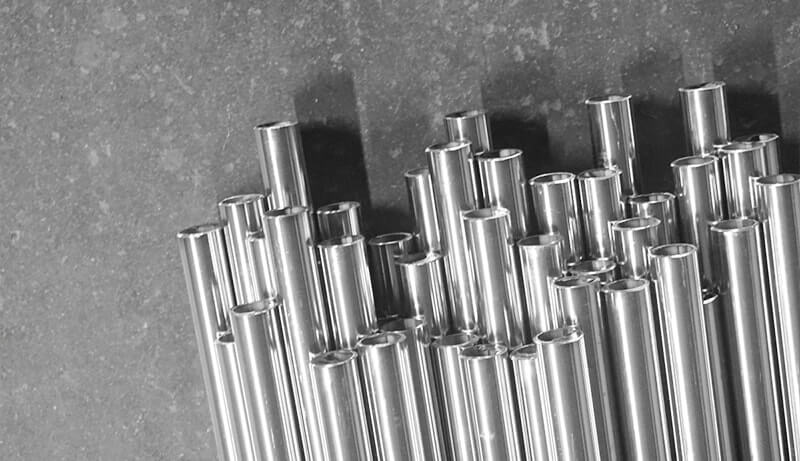


The corrosion resistance of 316 stainless steel is better than that of 304 stainless steel, and it has good corrosion resistance in the production process of pulp and paper. Moreover, 316 stainless steel is also resistant to erosion by marine and aggressive industrial atmospheres.
Generally speaking, there is not much difference between 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel in terms of chemical corrosion resistance, but there are differences in some specific media.
The stainless steel originally developed was 304, which is sensitive to pitting corrosion under certain circumstances. Adding an extra 2-3% molybdenum reduces this sensitivity, and thus 316 is born. In addition, this extra molybdenum can reduce the corrosion of some hot organic acids.
316 stainless steel has become almost the standard material in the food and beverage industry. Due to the worldwide shortage of molybdenum and the higher nickel content in 316 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel is more expensive than 304 stainless steel.
Pitting corrosion is a phenomenon mainly caused by deposition corrosion on the surface of stainless steel, which cannot form a protective layer of chromium oxide due to lack of oxygen.
Especially in small valves, there is little chance of deposits on the valve plate, so pitting corrosion is also rare.

In various types of water media (distilled water, drinking water, river water, boiler water, sea water, etc.), the corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel is almost the same, unless the content of chloride ions in the medium is very high, at this time 316 stainless steel will be more suitable.
In most cases, the corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel is not much different, but in some cases it may be very different, which needs to be analyzed in detail. Generally speaking, valve users should know it well, because they will choose the material of containers and pipes according to the conditions of the medium, and it is not recommended to recommend materials to users.
In intermittent use below 1600 degrees and continuous use below 1700 degrees, 316 stainless steel has good oxidation resistance. In the range of 800-1575 degrees, it is best not to use 316 stainless steel continuously, but when 316 stainless steel is used continuously outside this temperature range, the stainless steel has good heat resistance. The carbide precipitation resistance of 316L stainless steel is better than that of 316 stainless steel, and the above temperature range can be used.
Annealing is carried out in the temperature range of 1850-2050 degrees, then rapid annealing, and then rapid cooling. 316 stainless steel cannot be hardened by heat treatment.
316 stainless steel has good welding performance. All standard welding methods can be used for welding. According to the application, 316Cb, 316L or 309Cb stainless steel filler rods or welding rods can be used for welding. In order to obtain the best corrosion resistance, the welded section of 316 stainless steel needs to be annealed after welding. If 316L stainless steel is used, welding annealing is not required.
Among all steels, austenitic stainless steel has the lowest yield point. Therefore, in terms of mechanical properties, austenitic stainless steel is not the best material for the valve stem, because to ensure a certain strength, the diameter of the valve stem will increase. The yield point cannot be increased by heat treatment, but it can be increased by cold forming.
Due to the wide application of austenitic stainless steel, people have the wrong impression that all stainless steels are not magnetic. For austenitic stainless steel, it can basically be understood as non-magnetic, and it is true for quenched forged steel. But 304 processed by cold forming will be somewhat magnetic. For cast steel, if it is 100% austenitic stainless steel, it is not magnetic.
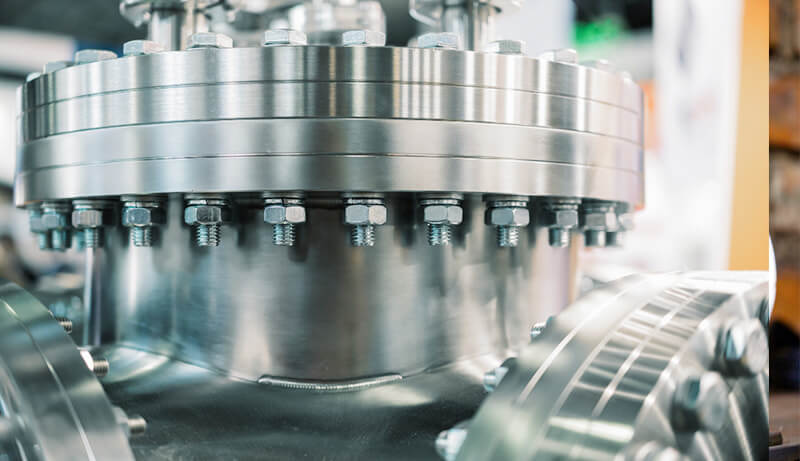
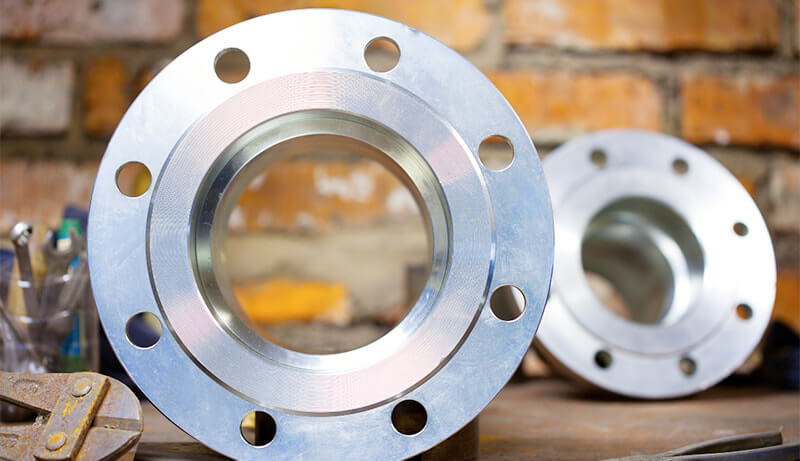


The corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel comes from the protective layer of chromium oxide formed on the metal surface. If the material is heated to a high temperature of 450°C to 900°C, the structure of the material changes and chromium carbides form along the crystal edges.
In this way, a protective layer of chromium oxide cannot be formed at the edge of the crystal, resulting in reduced corrosion resistance. This corrosion is called "intergranular corrosion".
As a result, 304L stainless steel and 316L stainless steel were developed to combat this corrosion. Both 304L stainless steel and 316L stainless steel have low carbon content, because the carbon content is reduced, so there will be no chromium carbide and no intergranular corrosion.
It should be noted that higher susceptibility to intergranular corrosion does not mean that non-low carbon materials are more likely to corrode. This sensitivity is also increased in high chlorine environments.
Please note that this phenomenon is due to high temperature (450°C-900°C). Usually soldering is the direct cause of reaching this temperature. For soft seat conventional butterfly valves it doesn't make much sense to use low carbon stainless steel since we don't weld on the disc, although most specifications will call for 304L or 316L stainless steel.
Why does stainless steel get rusty? When brown rust spots (spots) appear on the surface of stainless steel pipes, people are very surprised: they think that "stainless steel is rustless, and if it gets rusty, it is not stainless steel. It may be that there is a problem with the quality of the steel."
In fact, this is a one-sided misconception about the lack of understanding of stainless steel. Stainless steel also can get rusty under certain conditions.
Stainless steel has the ability to resist atmospheric oxidation—that is, it is not rusty, and it also has the ability to be corroded in media containing acids, alkalis, and salts—that is, corrosion resistance. But the size of its anti-corrosion ability is changed with the chemical composition of its steel itself, the state of reinforcement, service conditions and environmental medium type.
Like 304 steel pipes, in the atmosphere of dry cleansing, absolute good resistant to tarnishing ability is arranged, but it is moved on to riviera, in containing the sea fog of a large amount of salts, will soon get rusty; good. Therefore, not any kind of stainless steel can resist corrosion and rust in any environment.