Case
Home / Case / Experience / What is the difference between gate valve and globe valve?

Case
When the installation space is limited, you should pay attention to the selection. The gate valve can rely on the medium pressure to tightly seal with the sealing surface to achieve the effect of no leakage. When opening and closing, the sealing surfaces of the valve core and the valve seat are always in contact and friction with each other, so the sealing surface is easy to wear. When the gate valve is close to closing, the pressure difference between the front and rear of the pipeline is large, making the sealing surface wear more serious.
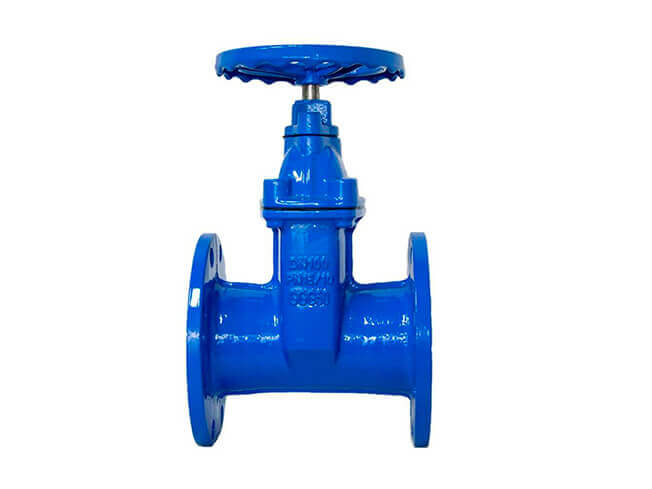
The structure of the gate valve will be more complex than that of the globe valve. From the appearance point of view, under the same diameter, the gate valve is taller than the globe valve, and the globe valve is longer than the gate valve. In addition, gate valves are divided into exposed stems and concealed stems. No shutoff valve.
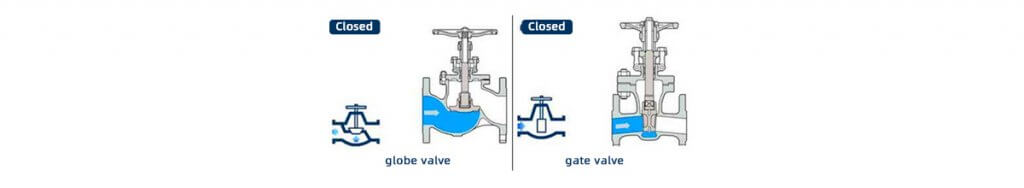
When the stop valve opens and closes, it has a rising stem type, which means that when you turn the handwheel, the handwheel will rotate and lift together with the valve stem. The gate valve rotates the handwheel to make the valve stem move up and down, while the position of the handwheel itself remains unchanged. The flow rates vary. Gate valves require fully open or fully closed, while stop valves do not. Globe valves have specified inlet and outlet directions; gate valves have no inlet and outlet direction requirements.
In addition, the gate valve only has two states: fully open or fully closed. The gate opening and closing stroke is large and the opening and closing time is long. The valve plate movement stroke of the stop valve is much smaller, and the valve plate of the stop valve can stop at a certain place during movement for flow adjustment. The gate valve can only be used for cutting off and has no other functions.
The stop valve can be used for both cutting off and flow adjustment. The fluid resistance of the stop valve is relatively large, and it is more laborious to open and close. However, because the distance between the valve plate and the sealing surface is short, the opening and closing stroke is short.
Because the gate valve can only be fully opened and fully closed, when it is fully opened, the medium flow resistance in the valve body channel is almost 0, so the opening and closing of the gate valve will be very labor-saving, but the distance between the gate plate and the sealing surface will be long, and the opening and closing time will be long.
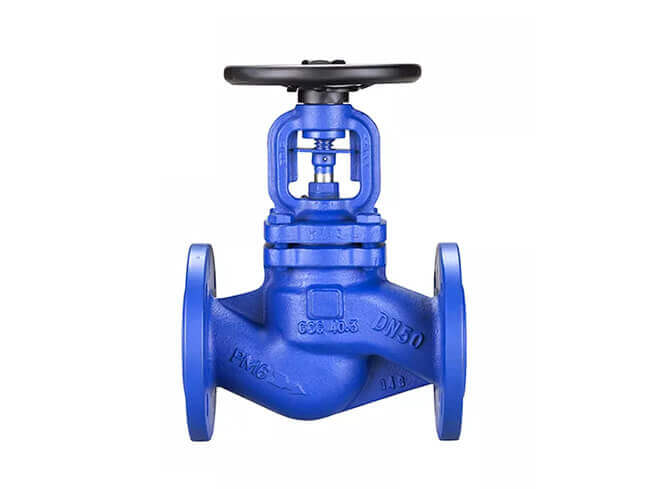



The gate valve has the same flow effect in both directions. There is no requirement for the inlet and outlet directions during installation, and the medium can flow in both directions. The stop valve needs to be installed strictly in accordance with the direction marked by the arrow on the valve body. There is also a clear regulation on the inlet and outlet directions of the stop valve. China's "Three Modernizations" of valves stipulates that the flow direction of the stop valve should be from top to down.
The stop valve has a low inlet and a high outlet. From the outside, it is obvious that the pipeline is not on the same phase level. The gate valve flow path is on a horizontal line. The stroke of the gate valve is larger than that of the globe valve.
From the perspective of flow resistance, the flow resistance of the gate valve is small when fully open, while the flow resistance of the load check valve is large. The flow resistance coefficient of ordinary gate valves is about 0.08~0.12, the opening and closing force is small, and the medium can flow in both directions. The flow resistance of ordinary stop valves is 3-5 times that of gate valves (official account: Pump Butler). When opening and closing, forced closing is required to achieve sealing. The valve core of the stop valve only contacts the sealing surface when it is completely closed, so the wear of the sealing surface is very small. Due to the large main flow force, the stop valve that requires an actuator should pay attention to the torque control mechanism adjustment.
There are two ways to install the stop valve. One is that the medium can enter from the bottom of the valve core. The advantage is that the packing is not under pressure when the valve is closed, which can extend the service life of the packing and can bear pressure in the pipeline in front of the valve. In this case, replace the packing; the disadvantage is that the driving torque of the valve is large, which is about 1 times that of the flow from above. The axial force on the valve stem is large and the valve stem is easy to bend. Therefore, this method is generally only suitable for small-diameter stop valves (under DN50). Stop valves above DN200 all use the method of medium flowing in from above.
The gate valve is a gate that opens and closes. The movement direction of the gate is perpendicular to the direction of the fluid. The gate valve can only be fully opened and fully closed, and cannot be adjusted or throttled.
Turn the handwheel and advance or retreat the thread between the handwheel and the valve stem to lift or lower the valve plate connected to the valve stem to open and close.
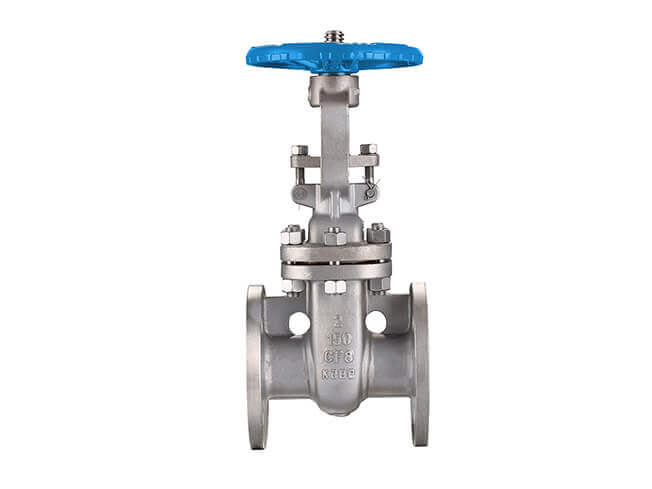
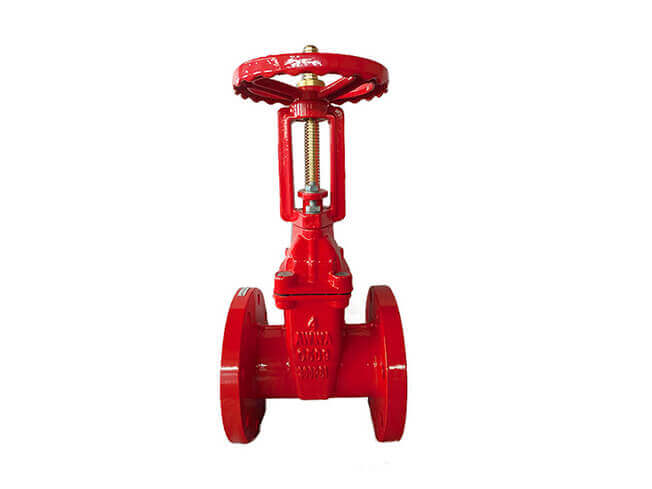



① The fluid resistance is small, and the sealing surface is less eroded and eroded by the medium.
②It takes less effort to open and close.
③The flow direction of the medium is not restricted, and there is no flow disturbance or pressure reduction.
④Simple shape, short structural length, good manufacturing process, and wide application range.
① It is easy to cause erosion and scratches between sealing surfaces, making maintenance difficult.
②The overall size is large, it requires a certain amount of space to open, and the opening and closing time is long.
③The structure is complex.
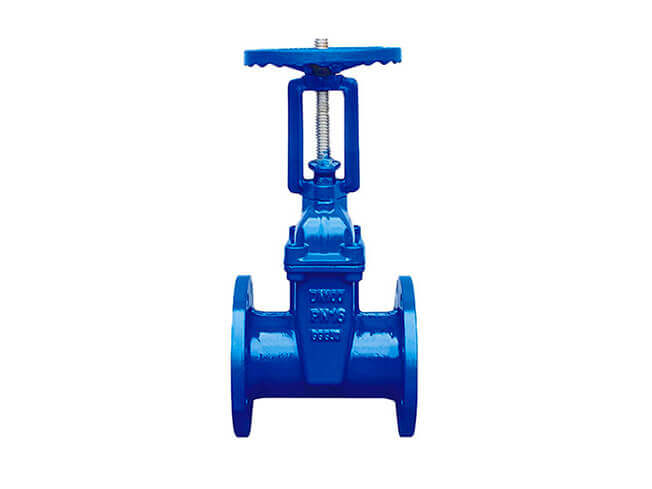
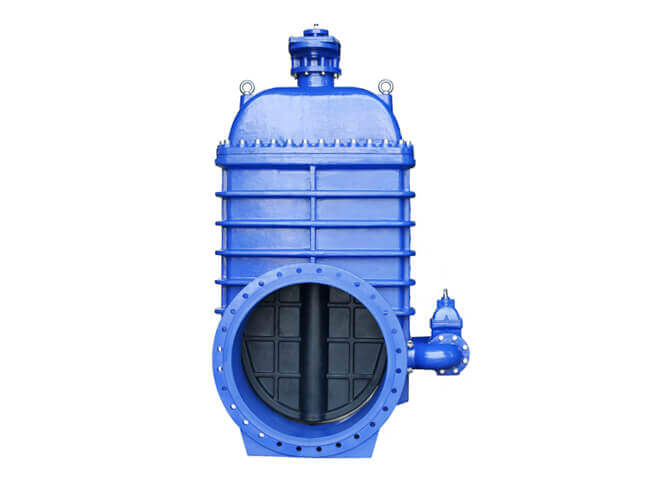
Concealed stem gate valve is also called rotating stem gate valve (also called concealed stem wedge gate valve). The valve stem nut is set on the gate plate. The rotation of the handwheel drives the valve stem to rotate, which lifts the gate plate. There is usually a trapezoidal thread at the bottom of the valve stem. The rotating movement is carried out through the thread at the bottom of the valve and the guide groove on the valve disc. It changes into linear motion, that is, the operating torque is changed into operating thrust.



When the valve is opened, when the lift height of the gate plate is equal to 1:1 times of the valve diameter, the fluid channel is completely unobstructed, but during operation, this position cannot be monitored. In actual use, the top of the valve stem is used as a mark, that is, the position that does not open, as its fully open position. In order to consider the locking phenomenon caused by temperature changes, the valve is usually opened to the top position and then retracted 1/2 to 1 turn as the fully open valve position. Therefore, the fully open position of the valve is determined by the position of the gate (i.e. stroke).
The advantage of this structure is that the height of the gate valve always remains unchanged, so the installation space is small, and it is suitable for gate valves with large diameters or limited installation space. This structure should be equipped with an opening and closing indicator to indicate the degree of opening and closing.
The disadvantage of this structure is that the valve stem thread is not only unable to be lubricated, but also directly eroded by the medium and easily damaged.
① The lead screw cannot be seen in valves with concealed stems, while the lead screw can be seen in valves with exposed stems.
② The lifting screw of the concealed stem flange gate valve only rotates without moving up and down. Only a rod is exposed, and its nut is fixed on the gate plate. The gate plate is lifted by the rotation of the screw rod, and there is no visible door frame; The lifting screw of the rising stem flange gate valve is exposed, and the nut is close to the handwheel and is fixed (does not rotate or move axially). The gate is lifted by rotating the screw. The screw and the gate only have relative rotational movement without any movement. Relative axial displacement, the appearance is a door-shaped bracket.
③ When the concealed stem valve is opened and closed, the steering wheel and the valve stem are connected together and are relatively immobile. It opens and closes by rotating the valve stem at a fixed point to drive the valve disc upward and lower the gate. The rising stem valve uses threaded transmission between the valve stem and the steering wheel to lift or lower the valve disc. To put it simply, in a rising stem valve, the valve disc moves up and down together with the valve stem, and the steering wheel is always at a fixed point.